parent
ab74a1bbb0
commit
ccad53b5b6
@ -0,0 +1,234 @@ |
||||
--- |
||||
ConstraintLayout 一篇就够了~ |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
#### 目录 |
||||
|
||||
1. 基本使用 |
||||
1. 相对位置 |
||||
2. 设置边距 |
||||
3. 水平/垂直偏移量 |
||||
4. 按比例设置 |
||||
5. 链 |
||||
6. GuideLine |
||||
2. 代码设置约束以及动画 |
||||
3. 优势 |
||||
4. 注意事项 |
||||
1. 可见性 |
||||
2. margin 负值问题 |
||||
3. 区分 0dp 、match_parent、warp_content |
||||
5. 参考 |
||||
|
||||
#### 前言 |
||||
|
||||
对于 ConstraintLayout,最开始看的郭大叔的 [Android新特性介绍,ConstraintLayout完全解析](https://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/53122387),但是由于自身原因更倾向于直接在 xml 里面写。之后又看了鸿洋的 [ConstraintLayout 完全解析 快来优化你的布局吧](https://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/78011599?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral),还不错,但是有些知识的遗漏。 |
||||
|
||||
如果你一点没接触过约束布局,以上两篇是不错的选择。 |
||||
|
||||
本文把 ConstraintLayout 的使用细分了一下,**对于控件的学习,一定要自己动手写!** |
||||
|
||||
看完自己动手敲一遍,基本上就可以在项目中尝试用了~ |
||||
|
||||
本文偏总结,想要看每个属性的预览图,可以参考:[ConstraintLayout在项目中实践与总结](https://www.jianshu.com/p/f110b4fcfe93) |
||||
|
||||
我也是看了这篇文章受益匪浅,在这里诚谢作者的无私奉献~ |
||||
|
||||
最后,直接 fork [https://github.com/googlesamples/android-ConstraintLayoutExamples](https://github.com/googlesamples/android-ConstraintLayoutExamples) |
||||
|
||||
#### 基本使用 |
||||
|
||||
##### 相对位置 |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf |
||||
layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf |
||||
... |
||||
layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf //文字的 baseline 对齐 |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
这一部分的使用和 RelativeLayout 使用一致,设置控件的相对位置。 |
||||
|
||||
##### 设置边距 |
||||
|
||||
边距分为普通边距和依赖控件被 Gone 掉后的边距属性: |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
//普通边距 |
||||
android:layout_marginStart |
||||
android:layout_marginLeft |
||||
... |
||||
//依赖控件被 GONE 掉后的边距属性 |
||||
android:layout_goneMarginStart |
||||
android:layout_goneMarginLeft |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
##### 水平/垂直偏移 |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
//值为 0~1 之间 |
||||
layout_constraintHorizontal_bais //水平偏移 |
||||
layout_constraintVertical_bais //垂直偏移 |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
##### 按比例设置 |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
//设置控件宽高比,前提是至少有一个尺寸是 0dp |
||||
//值可以是 float,比如 0.5,表示宽高比 |
||||
//也可以是形如:5:3,表示宽高比 |
||||
layout_constraintDimentionRatio |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
如果宽高都设置了 0dp,那么控件会在满足比例的情况下尽可能填满父布局。 |
||||
|
||||
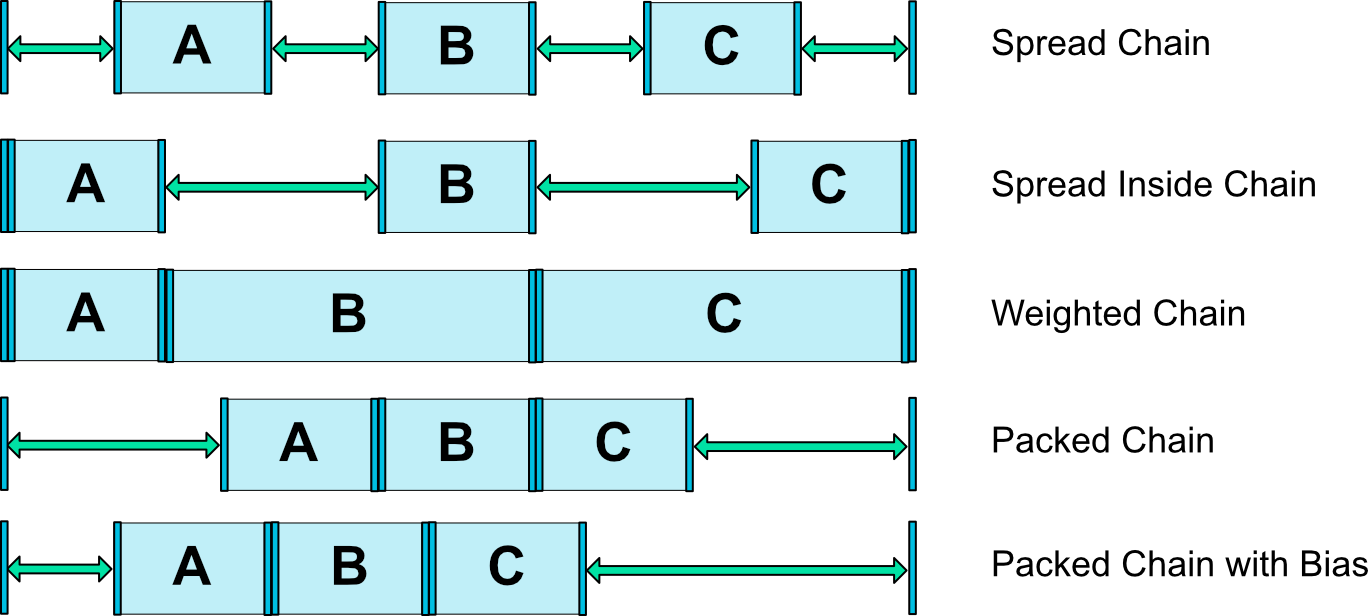
##### 链 |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
//链提供了在一个维度上管理一组控件的方式,链的属性由链头控制 |
||||
//它有三个值: spread、spread_inside、packed,默认值是 spread |
||||
layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle |
||||
layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
至于不同的样式会是什么效果,这里直接盗官网图说明: |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
##### Guideline |
||||
|
||||
Guideline 可以理解为布局辅助线。 |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
<android.support.constraint.Guideline |
||||
android:id="@+id/vertical_line" |
||||
android:orientation="vertical" |
||||
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5" |
||||
android:layout_width="wrap_content" |
||||
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> |
||||
|
||||
<android.support.constraint.Guideline |
||||
android:id="@+id/horizontal_line" |
||||
android:orientation="horizontal" |
||||
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5" |
||||
android:layout_width="wrap_content" |
||||
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
它有垂直和水平两个方向,垂直宽度为 0,高度为父容器;水平高度为 0,宽度为父容器。 |
||||
|
||||
放置 Guideline 的三种方式: |
||||
|
||||
1. layout_constraintGuide_begin |
||||
|
||||
给定左边或顶部一个固定距离 |
||||
|
||||
2. layout_constraintGuide_end |
||||
|
||||
给定距离右边或底部一个固定距离 |
||||
|
||||
3. layout_constraintGuide_percent |
||||
|
||||
给定宽高一个百分比距离 |
||||
|
||||
#### 代码设置约束 |
||||
|
||||
用代码设置约束着实是一个坑! |
||||
|
||||
通过 ConatraintSet,允许在代码中进行设置约束,进行布局变换。 |
||||
|
||||
这里,可以直接看前言给的官方示例了,效果如下: |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
代码两三行就完了,就是两个布局,布局里面的 View id 一致,添加过渡效果只需要一行代码: |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
TransitionManager.beginDelayedTransition(mConstraintLayout); |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
就不多说了,直接 fork Simples 吧。 |
||||
|
||||
#### 优势 |
||||
|
||||
约束布局减少了布局嵌套,在绘制渲染上提供了更好的性能。根据 Google 提供的数据表明,ConstraintLayout 在测量/布局阶段的性能比 RelativeLayout 大约高 40%。 |
||||
|
||||
同时,由于各种百分比的属性,适配性比传统布局好。 |
||||
|
||||
#### 注意事项 |
||||
|
||||
1. 可见性 |
||||
|
||||
约束布局中的可见性和其他布局相比不太一样,当控件设为 gone 时,被认为尺寸为 0,可以理解为布局上的一个点。若 gone 的控件对其它控件有约束,约束保留并生效,但是所有边距会清零。 |
||||
|
||||
2. margin 负值问题 |
||||
|
||||
在其他布局中,可以设置 margin 负值来达到布局重叠的效果,而在约束布局中设置 margin 负值不生效,那如何才能实现布局重叠的效果呢? |
||||
|
||||
可以通过辅助线和 1dp View 来实现,内在思想都是一样的。 |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout |
||||
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" |
||||
android:layout_width="match_parent" |
||||
android:layout_height="match_parent" |
||||
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"> |
||||
<Button |
||||
android:id="@+id/btn" |
||||
android:text="按钮" |
||||
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" |
||||
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" |
||||
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" |
||||
android:layout_width="0dp" |
||||
android:layout_height="200dp" /> |
||||
|
||||
//辅助 View |
||||
<View |
||||
android:id="@+id/view" |
||||
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@id/btn" |
||||
android:layout_marginBottom="40dp" |
||||
android:visibility="invisible" |
||||
android:layout_width="match_parent" |
||||
android:layout_height="1dp" /> |
||||
<Button |
||||
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/view" |
||||
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" |
||||
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" |
||||
android:text="按钮" |
||||
app:layout_constraintWidth_max="200dp" |
||||
android:layout_width="0dp" |
||||
android:layout_height="100dp" /> |
||||
|
||||
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
3. 0dp、match_parent、warp_content 区别 |
||||
|
||||
当设置 0 dp 的时候,它会基于约束最终确定大小。而设置 match_parent 充满父布局,此时设置的约束都不会生效。 |
||||
|
||||
基于约束确定大小有三种: |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
//设置约束宽/高最小值 |
||||
layout_constraintWidth_min |
||||
layout_constraintHeight_min |
||||
//设置约束宽/高最大值 |
||||
layout_constraintWidth_max |
||||
layout_constraintHeight_max |
||||
//根据百分比设置 |
||||
//需要现开启百分比模式 |
||||
layout_constraintWidth_default = "percent" |
||||
layout_constraintHeight_default = "percent" |
||||
layout_constraintWidth_percent = "0.5" |
||||
layout_constraintHeight_percent = "0.5" |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
对于 warp_content,它会根据内容计算合适大小,所以添加约束是不起效果的,但是我们也可以强制约束: |
||||
|
||||
```java |
||||
layout_constraintWidth = "true" |
||||
layout_constraintHeight = "true" |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
#### 参考 |
||||
|
||||
[ConstraintLayout在项目中实践与总结](https://www.jianshu.com/p/f110b4fcfe93) |
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 174 KiB |
Loading…
Reference in new issue