You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
430 lines
17 KiB
430 lines
17 KiB
---
|
|
自定义 View
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
#### 目录
|
|
|
|
1. 前言
|
|
2. 基础知识储备
|
|
- 坐标系
|
|
- 颜色
|
|
3. 自定义 View
|
|
- 分类和流程
|
|
- Canvas 之常用 API
|
|
- MotionEvent
|
|
- 手势检测
|
|
4. 常见问题汇总
|
|
- 处理 warp_content
|
|
- 处理 padding
|
|
- 处理 margin
|
|
5. 实战之酷炫进度条
|
|
6. 参考
|
|
|
|
#### 前言
|
|
|
|
自定义 View 系列直接看 [GcsSloop 自定义 View 系列](http://www.gcssloop.com/customview/CustomViewIndex/) 就可以了,熟悉了 API 能自定义简单的 View,该系列最后都一个例子来练习,可以参考 [https://github.com/Omooo/ChartsDemo](https://github.com/Omooo/ChartsDemo) 中的代码,没错,也是我的~
|
|
|
|
这些知识长时间不实践就忘的差不多了,于是再来一遍。
|
|
|
|
#### 基础知识储备
|
|
|
|
##### 坐标系
|
|
|
|
Android 中的屏幕坐标系是以屏幕的左上角为坐标原点的,向右为 x 正轴,向下是 y 正轴。
|
|
|
|
这里就要提一下 View 的坐标系了,View 的坐标系统是相对于父控件而言的:
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
getTop() //获取子 View 左上角到父 View 顶部的距离
|
|
getLeft() //获取子 View 左上角到父 View 左边的距离
|
|
getBottom() //获取子 View 右下角到父 View 顶部的距离
|
|
getRight() //获取子 View 右上角到父 View 左边的距离
|
|
|
|
getBottom() - getTop() = View 的高
|
|
getRight() - getLeft() = View 的宽
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
MotionEvent 中的 getXxx 和 getRawXxx 的区别:
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
event.getX() //触摸点相对于其所在 View 坐标系的坐标
|
|
event.getY()
|
|
|
|
event.getRawX() //触摸点相对于屏幕坐标系的坐标
|
|
event.getRawY()
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
##### 颜色
|
|
|
|
Android 支持的颜色模式有:
|
|
|
|
| 颜色模式 | 备注 |
|
|
| -------- | -------------------- |
|
|
| ARGB8888 | 四通道高精度(32位) |
|
|
| ARGB4444 | 四通道低精度(16位) |
|
|
| RGB565 | 屏幕默认模式(16位) |
|
|
|
|
RGB 代表红绿蓝三原色,A 代表透明度,后面的数值表示该类型用多少位二进制来描述。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
#f00 //低精度 - 不带透明通道红色
|
|
#af00 //低精度 - 带透明通道红色
|
|
#ff0000 //高精度 - 不带透明通道红色
|
|
#aaff0000 //高精度 - 带透明通道红色
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
有了基础知识储备,接下来就开始进入自定义 View 了~~~
|
|
|
|
#### 自定义 View 分类和流程
|
|
|
|
自定义 View 可以分为两类:一类是自定义 ViewGroup,另一种是自定义 View。自定义 ViewGroup 一般是利用已有的 View 按照特定的布局方式来实现新的组件,比如带自动换行的水平的线性布局等。自定义 View 一般是由于没有现成的 View 可以使用,需要自己实现 onDraw 来绘制。
|
|
|
|
自定义 View 的流程也是一个通用的套路:
|
|
|
|
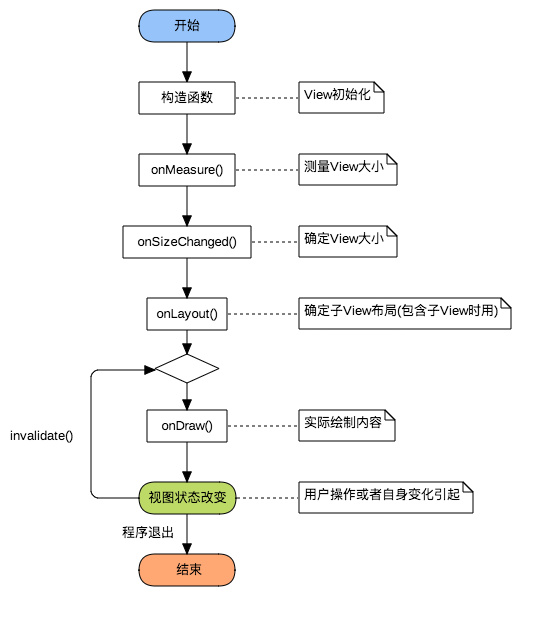
|
|
|
|
##### 构造函数
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
public class MyCustomView extends View {
|
|
|
|
//在 Activity 中以 new MyCustomView(this) 创建 View
|
|
public MyCustomView(Context context) {}
|
|
|
|
//在 xml 中创建 View
|
|
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {}
|
|
|
|
//为 View 指定样式
|
|
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {}
|
|
|
|
//API > 21
|
|
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
我们只需要实现前两个构造函数即可,AttributeSet 用于获取自定义属性等。
|
|
|
|
##### onMeasure()
|
|
|
|
用于测量 View 的大小。
|
|
|
|
你可能会问,既然我们在 xml 里面可以指定 View 的宽高尺寸,为什么还需要自己测量呢?
|
|
|
|
这是因为,View 的大小不仅由自身所决定,同时也会受父控件的影响,比如我们设置 warp_content 或 match_parent。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
|
|
//获取宽度尺寸和宽度测量模式
|
|
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
onMeasure 中的参数可以翻译成测量规格,它有两部分组成:宽高实际尺寸和宽高测量模式。
|
|
|
|
测量模式有三种:
|
|
|
|
| 模式 | 二进制值 | 描述 |
|
|
| ----------- | -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
| UNSPECIFIED | 00 | 默认值,父控件没有给子 View 任何限制,子 View 可以设置为任意大小,一般用在系统中,我们可以不管 |
|
|
| EXACTLY | 01 | 表示父控件已经确切指定了子 View 的大小,对应于 match_parent 和 确切数值 100dp |
|
|
| AT_MOST | 10 | 表示子 View 的大小存在上限,一般是父 View 大小,对应于 warp_content |
|
|
|
|
所以在测量规格中,只需要两个 bit 就能表示完测量模式,而事实上正是这样做的,测量规格是一个 int 数值,32位,前两位表示测量模式,后三十位表示测量数值。
|
|
|
|
##### onSizeChanged()
|
|
|
|
在视图大小发生改变时调用。
|
|
|
|
既然在测量完 View 并使用 setMeasuredDimension 函数之后 View 的大小基本上已经确定了,那为什么还要再次确认 View 的大小呢?
|
|
|
|
这是因为 View 的大小不仅由 View 本身控制,而且受父控件的影响,所以我们在确定 View 大小的时候最好使用系统提供的 onSizedChanged 回调函数。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
|
|
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
w、h 即是 View 最终的大小。
|
|
|
|
##### onLayout()
|
|
|
|
确定布局的函数是 onLayout,它用于确定子 View 的位置,在定义 ViewGroup 中会用到,它调用的是子 View 的 layout 函数。
|
|
|
|
在自定义 ViewGroup 中,onLayout 一般是循环取出子 View,然后经过计算得出各个子 View 位置的坐标值,然后用以下函数设置子 View 位置。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
child.layout(l,t,r,b)
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
##### onDraw()
|
|
|
|
onDraw 是实际绘制的部分,使用 Canvas 绘制。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
|
|
super.onDraw(canvas);
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### 自定义 View 之 Canvas 常用 API
|
|
|
|
| 操作类型 | 相关 API | 备注 |
|
|
| ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------ |
|
|
| 绘制颜色 | drawColor、drawRGB、drawARGB | 使用单一颜色填充整个画布 |
|
|
| 绘制基本图形 | drawPoint、drawPoints、drawLine、drawLines、drawRect、drawRoundRect、drawOval、drawCircle、drawArc | 绘制点、线、矩形、圆角矩形、椭圆、圆、圆弧 |
|
|
| 绘制图片 | drawBitmap、drawPicture | 绘制位图和图片 |
|
|
| 绘制路径 | drawPath | 绘制路径,绘制贝塞尔曲线 |
|
|
| 画布裁剪 | clipPath、clipRect | 设置画布的显示区域 |
|
|
| 画布变换 | translate、scale、rotate、skew | 位移、缩放、旋转、错切 |
|
|
|
|
#### MotionEvent
|
|
|
|
| 事件 | 简介 |
|
|
| ------------- | ---------------------------------- |
|
|
| ACTION_DOWN | 手指初次接触屏幕时触发 |
|
|
| ACTION_MOVE | 手指在屏幕上滑动时触发,会多次触发 |
|
|
| ACTION_UP | 手指离开屏幕时触发 |
|
|
| ACTION_CANCEL | 事件被上层拦截时触发 |
|
|
|
|
这里主要说下 ACTION_CANCEL,它的触发条件是事件被上层拦截。但是我们知道,在事件分发中,如果父 View 拦截了事件,那么子 View 是收不到任何事件的。所以这个 ACTION_CANCEL 的正确触发条件是:
|
|
|
|
**只有父 View 回收事件处理权的时候,子 View 才会收到一个 ACTION_CANCEL 事件。**
|
|
|
|
举个例子:
|
|
|
|
上层 View 是一个 RecyclerView,它收到了一个 ACTION_DOWN 事件,由于这可能是个点击事件,所以它先传递给了对应的 ItemView,询问 ItemView 是否需要这个事件,然后接下来又传递过来一个 ACTION_MOVE 事件,且移动的方向和 RecyclerView 的可滑动方向一致,这时候 RecyclerView 判断这个事件是滚动事件,于是要回收事件处理权,这时候对应的 ItemView 就会收到一个 ACTION_CANCEL,并且不会再收到后续事件。
|
|
|
|
#### 手势检测(GestureDetector)
|
|
|
|
GestureDetector 可以使用 MotionEvents 检测各种手势和事件,使用起来也很简单~
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
final GestureDetector detector = new GestureDetector(this, new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener() {
|
|
@Override
|
|
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
|
|
Toast.makeText(WidgetActivity.this, "双击事件", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
|
|
return super.onDoubleTap(e);
|
|
}
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
mButton.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
|
|
@Override
|
|
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
|
|
return detector.onTouchEvent(event);
|
|
}
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### 常见问题汇总
|
|
|
|
##### 处理 warp_content
|
|
|
|
1. 自定义 View 的处理
|
|
|
|
如果我们不处理自定义 View 中的 warp_content,那么它和 match_parent 的效果一样。这里我们需要在 onMeasure() 里面做特殊处理:
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
|
|
//获取宽度尺寸和宽度测量模式
|
|
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
int defaultWidth = 200; //默认值
|
|
int defaultHeight = 200;
|
|
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
|
|
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(defaultWidth, defaultHeight);
|
|
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(defaultWidth, heightSize);
|
|
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, defaultHeight);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
可以看到,其实我们只是当是 warp_content 的时候设置一个默认值,但是这样不灵活,我们可以在自定义属性中设置。其次,我们可以参考系统对 TextView 的设置,它会根据文字的大小来设置默认宽高。
|
|
|
|
2. 自定义 ViewGroup 的处理
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
|
|
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
//将所有的子 View 进行测量,这会触发每个子 View 的 onMeasure
|
|
//measureChild 是对单个 View 进行测量
|
|
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
int childCount = getChildCount();
|
|
if (childCount == 0) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
|
|
} else {
|
|
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
int height = getTotalHeight(); //获取子 View 高度加和
|
|
int width = getMaxChildWidth(); //获取子 View 的最大宽度
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
|
|
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, getTotalHeight());
|
|
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(getMaxChildWidth(), heightSize);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
这里我们以自定义一个垂直的线性布局为例,当 ViewGroup 是 warp_content 的时候,高度为子 View 的高度和,宽度为子 View 中的最大宽度。
|
|
|
|
##### 处理 padding
|
|
|
|
1. 自定义 View 的处理
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
|
|
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
|
|
Rect rect = new Rect(0, 0, 100, 100);
|
|
Rect rect1 = new Rect(0 + getPaddingLeft(), 0 + getPaddingTop(), 100 - getPaddingRight(), 100 - getPaddingBottom());
|
|
canvas.drawRect(rect, mPaint);
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
2. 自定义 ViewGroup 的处理
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
|
|
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
//将所有的子 View 进行测量,这会触发每个子 View 的 onMeasure
|
|
//measureChild 是对单个 View 进行测量
|
|
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
|
|
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
|
|
|
|
//获取子 View 高度加和 padding 值
|
|
int height = getTotalHeight() + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
|
|
//获取子 View 的最大宽度加 padding 值
|
|
int width = getMaxChildWidth() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
|
|
|
|
int childCount = getChildCount();
|
|
if (childCount == 0) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
|
|
} else {
|
|
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(Math.min(width, widthSize), Math.min(height, heightSize));
|
|
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, Math.min(height, heightSize));
|
|
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
|
|
setMeasuredDimension(Math.min(width, widthSize), heightSize);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
##### 处理 margin
|
|
|
|
自定义 View 里 margin 是生效的,无需处理,只有 ViewGroup 才需要处理 margin。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
|
|
int count = getChildCount();
|
|
int currentHeight = t;
|
|
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
|
|
View child = getChildAt(i);
|
|
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
|
|
int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
|
|
int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
|
|
child.layout(l + lp.leftMargin, currentHeight + lp.topMargin, l + width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin, currentHeight + height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
|
|
currentHeight += height;
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
|
|
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### 实战
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
public class MyProgressView extends View {
|
|
|
|
private Paint mPaint;
|
|
private int mWidth;
|
|
private int mHeight;
|
|
private int textPadding = 5;
|
|
private int progress = 0;
|
|
|
|
public MyProgressView(Context context) {
|
|
super(context);
|
|
initPaint();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
public MyProgressView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
|
|
super(context, attrs);
|
|
initPaint();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
private void initPaint() {
|
|
mPaint = new Paint();
|
|
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
|
|
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
|
|
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
|
|
mPaint.setTextSize(14);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
|
|
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
|
|
mWidth = w;
|
|
mHeight = h;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
|
|
super.onDraw(canvas);
|
|
String text = progress + "%";
|
|
float textWidth = mPaint.measureText(text) + textPadding;
|
|
Rect rect = new Rect();
|
|
mPaint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), rect);
|
|
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
|
|
|
|
canvas.drawLine(0, mHeight / 2, progress * ((mWidth - textWidth) / 100), mHeight / 2, mPaint);
|
|
canvas.drawText(text, progress * ((mWidth - textWidth) / 100) + textPadding, (mHeight - rect.height()) / 2 + 2 * textPadding, mPaint);
|
|
mPaint.setColor(Color.GRAY);
|
|
canvas.drawLine(progress * ((mWidth - textWidth) / 100) + textWidth + textPadding, mHeight / 2, mWidth, mHeight / 2, mPaint);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
public void setProgress(int progress) {
|
|
if (progress > 100) {
|
|
progress = 100;
|
|
} else if (progress < 0) {
|
|
progress = 0;
|
|
}
|
|
this.progress = progress;
|
|
postInvalidate();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### 参考
|
|
|
|
[GcsSloop 自定义 View 系列](http://www.gcssloop.com/category/customview)
|
|
|
|
[Android 自定义 View 之 margin 和 padding 的处理](https://blog.csdn.net/u012732170/article/details/55045472) |