20 KiB
目录
-
思维导图
-
SharedPreference
-
常见问题
-
基本使用以及适用范围
-
核心原理以及源码分析
-
注意事项以及优化建议
-
-
参考
思维导图
SharedPreference
常见问题
- SharedPreferences 是如何初始化的,它会阻塞线程嘛?如果会,是什么原因。而且每次获取 SP 对象真的会很慢吗?
- commit 和 apply 的区别,commit 一定会在主线程操作嘛?
- SP 在使用时需要注意哪些问题,以及有什么优化点呢?
基本使用以及适用范围
基本使用:
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = this.getSharedPreferences(getLocalClassName(), MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = sharedPreferences.edit();
editor.putString("key", "value");
editor.apply();
SharedPreferences 本身是一个接口,程序无法直接创建 SharedPreferences 实例,只能通过 Context 提供的 getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode) 方法来获取 SharedPreferences 实例,name 表示要存储的 xml 文件名,第二个参数直接写 Context.MODE_PRIVAT,表示该 SharedPreferences 数据只能被本应用读写。当然还有 MODE_WORLD_READABLE 等,但是已经被废弃了,因为 SharedPreference 在多进程下表现并不稳定。
适用范围:
保存少量的数据,且这些数据的格式简单,适用保存应用的配置参数,但不建议使用 SP 来存储大规模数据,可能会降低性能。
核心原理以及源码分析
核心原理:
保存基于 XML 文件存储的 key-value 键值对数据,在 /data/data/<package name>/shared_prefs 目录下。
SharedPreferences 本身只能获取数据而不支持存储和修改,存储修改是通过 SharedPreferences.Editor 来实现的,它们两个都只是接口,真正的实现在 SharedPreferencesImpl 和 EditorImpl 。
源码分析:
在此之前,我们先看 ContextImpl 中的一个静态成员变量:
/*
* String:包名,File:SP 文件,SharedPreferencesImpl:SP 实例对象
*/
private static ArrayMap<String, ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl>> sSharedPrefsCache;
因为一个进程只会存在一个 ContextImpl.class 对象,所以同一个进程内的所有 SharedPreferences 都保存在这个静态列表中。我们在看它的初始化:
private ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked() {
if (sSharedPrefsCache == null) {
sSharedPrefsCache = new ArrayMap<>();
}
final String packageName = getPackageName();
ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> packagePrefs = sSharedPrefsCache.get(packageName);
if (packagePrefs == null) {
packagePrefs = new ArrayMap<>();
sSharedPrefsCache.put(packageName, packagePrefs);
}
return packagePrefs;
}
sSharedPrefsCache 是一个 ArrayMap,它存储的是包名和 packagePrefs 的映射关系,而 packagePrefs 存储的是 SharedPreferences 文件与 SharedPreferences 实例对象之间的映射关系。
这里为什么要把 packageName 作为 key 呢?那是因为一个进程可以有多个 Android 应用,所以需要用包名来区分它们,在这里感谢 @虾饺哥哥 的指正和淳淳教诲。
这里,可以稍微总结一下,sSharedPrefsCache 会保存加载到内存中的 SharedPreferences 对象,当用户需要获取 SP 对象的时候,首先会在 sSharedPrefsCache 中查找,如果没找到,就创建一个新的 SP 对象添加到 sSharedPrefsCache 中,并且以当前应用的包名为 key。
除此之外,需要注意的是,ContextImpl 类中并没有定义将 SharedPreferences 对象移除 sSharedPrefsCache 的方法,所以一旦加载到内存中,就会存在直至进程销毁。相对的,也就是说,SP 对象一旦加载到内存,后面任何时间使用,都是从内存中获取,不会再出现读取磁盘的情况。
然后在看 ContextImpl#getSharedPrefenerces 方法:
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode) {
//...
File file;
synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {
if (mSharedPrefsPaths == null) {
mSharedPrefsPaths = new ArrayMap<>();
}
file = mSharedPrefsPaths.get(name);
if (file == null) {
file = getSharedPreferencesPath(name);
mSharedPrefsPaths.put(name, file);
}
}
return getSharedPreferences(file, mode);
}
mSharedPrefsPath 记录了所有的 SP 文件,以文件名为 key,具体文件为 value 的 map 结构。根据传入的 name 查找是否有这个文件,若没有就创建并添加到 mSharedPrefsPaths 中,若存在就跳到下面这个方法了:
ContextImpl#getSharedPreferences:
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(File file, int mode) {
SharedPreferencesImpl sp;
synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {
final ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> cache = getSharedPreferencesCacheLocked();
sp = cache.get(file);
if (sp == null) {
checkMode(mode);
if (getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
if (isCredentialProtectedStorage()
&& !getSystemService(UserManager.class)
.isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(UserHandle.myUserId())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("SharedPreferences in credential encrypted "
+ "storage are not available until after user is unlocked");
}
}
sp = new SharedPreferencesImpl(file, mode);
cache.put(file, sp);
return sp;
}
}
if ((mode & Context.MODE_MULTI_PROCESS) != 0 ||
getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
sp.startReloadIfChangedUnexpectedly();
}
return sp;
}
原来是根据传入的 file 从 ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> 拿到 SharedPreferences(SharedPreferencesImpl) 实例。关键代码其实并不多,但是我还是把所有代码都贴上了,因为这里我们能看到一个兼容性问题以及多进程问题,兼容性问题是指如果在 Android O 及更高版本中,通过传入的 file 拿到的 SharedPreferences 实例为空,说明该文件目录是用户无权限访问的,会直接抛出一个异常。多进程问题是指在 Context.MODE_MULTI_PROCESS 下,可能存在记录丢失的情况。
拿到了 SharedPreferencesImpl 实例之后,看一下其构造方法:
SharedPreferencesImpl(File file, int mode) {
mFile = file;
mBackupFile = makeBackupFile(file);
mMode = mode;
mLoaded = false;
mMap = null;
mThrowable = null;
startLoadFromDisk();
}
private void startLoadFromDisk() {
synchronized (mLock) {
mLoaded = false;
}
//直接创建一个线程来读取磁盘文件
new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load") {
public void run() {
loadFromDisk();
}
}.start();
}
private void loadFromDisk() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mLoaded) {
return;
}
if (mBackupFile.exists()) {
mFile.delete();
mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile);
}
}
//...
synchronized (mLock) {
mLoaded = true;
mThrowable = thrown;
//...
}
}
果然,它是在子线程读取的磁盘文件,所以说 SP 对象初始化过程本身的确不会造成主线程的阻塞。但是真的不会阻塞嘛?这里需要注意,在读取完磁盘文件后,把 mLoaded 置为 true,继续往下看。
我们知道,写 SP 只能通过 SP.Editor,源码如下:
SharedPreferencesImpl#edit:
@Override
public Editor edit() {
synchronized (mLock) {
awaitLoadedLocked();
}
return new EditorImpl();
}
private void awaitLoadedLocked() {
//...
while (!mLoaded) {
try {
mLock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException unused) {
}
}
//...
}
从上面代码可知,只有子线程从磁盘加载完数据之后,mLoaded 才会被置为 true,所以说虽然从磁盘读取数据是在子线程中进行并不会阻塞主线程,但是如果文件在读取之前获取某个 SharedPreferences 的值,那么主线程就可能被阻塞住,直到子线程加载完文件为止,所以说保存的 SP 文件不宜太大。
EditorImpl 就是 Editor 真正的实现类,在这里面我们能看到我们经常使用的 putXxx 方法:
//...
private final Map<String, Object> mModified = new HashMap<>();
private boolean mClear = false;
@Override
public Editor putString(String key, @Nullable String value) {
synchronized (mEditorLock) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
@Override
public Editor putInt(String key, int value) {
synchronized (mEditorLock) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
然后就是执行提交操作了,分两种,一种是 commit,一种是 apply,这里我把两个方法放在一块展示,便于查看区别:
EditorImpl#commit / apply:
public boolean commit() {
//1. 提交修改到内存中
MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
//2. 调用 enqueueDiskWrite 方法,注意第二个参数为 null
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(
mcr, null /* sync write on this thread okay */);
try {
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return false;
} finally {
//...
}
notifyListeners(mcr);
return mcr.writeToDiskResult;
}
public void apply() {
//1. 提交修改到内存中
final MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
final Runnable awaitCommit = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
};
QueuedWork.addFinisher(awaitCommit);
Runnable postWriteRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
awaitCommit.run();
QueuedWork.removeFinisher(awaitCommit);
}
};
//2. 调用 enqueueDiskWrite 方法,注意第二个参数为 postWriteRunnable
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(mcr, postWriteRunnable);
notifyListeners(mcr);
}
可以看到 commit 和 apply 都会先把修改提交到内存中,然后在在通过 enqueueDiskWrite 将要写入磁盘的任务进行排队, commitToMemory 方法源码就不贴了,其实就是将数据插入到 mMap 中,这是对内存中的数据进行更新,着重看一下 enqueueDiskWrite 方法:
SharedPreferencesImpl#enqueueDiskWrite 方法:
/**
* Enqueue an already-committed-to-memory result to be written
* to disk.
*
* They will be written to disk one-at-a-time in the order
* that they're enqueued.
*
* @param postWriteRunnable if non-null, we're being called
* from apply() and this is the runnable to run after
* the write proceeds. if null (from a regular commit()),
* then we're allowed to do this disk write on the main
* thread (which in addition to reducing allocations and
* creating a background thread, this has the advantage that
* we catch them in userdebug StrictMode reports to convert
* them where possible to apply() ...)
*/
private void enqueueDiskWrite(final MemoryCommitResult mcr,
final Runnable postWriteRunnable) {
final boolean isFromSyncCommit = (postWriteRunnable == null);
final Runnable writeToDiskRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (mWritingToDiskLock) {
writeToFile(mcr, isFromSyncCommit);
}
synchronized (mLock) {
mDiskWritesInFlight--;
}
if (postWriteRunnable != null) {
postWriteRunnable.run();
}
}
};
// Typical #commit() path with fewer allocations, doing a write on
// the current thread.
if (isFromSyncCommit) {
boolean wasEmpty = false;
synchronized (mLock) {
wasEmpty = mDiskWritesInFlight == 1;
}
//直接在当前执行 run 是有两个条件的,即来自 commit 并且 wasEmpty 为 true
if (wasEmpty) {
writeToDiskRunnable.run();
return;
}
}
QueuedWork.queue(writeToDiskRunnable, !isFromSyncCommit);
}
敲黑板,这是重点了。我保留了注释,从注释可以看出,首先第二个参数如果为 null 就说明来自 commit,如果非空就说明来自 apply。然后通过构造一个 writeToDiskRunnable ,那么什么时候它会 run 呢?那就是当方法调用来自 commit 并且 mDiskWritesInFlight == 1,这个 mDiskWritesInFlight 是在哪赋值的呢?
private int mDiskWritesInFlight = 0;
private MemoryCommitResult commitToMemory() {
//...
mDiskWritesInFlight++;
//...
}
嘿,这就清楚了,前面我们说过不管是 commit 还是 apply 都会先把修改提交到内存中,然后 mDiskWritesInFlight++,然后在每次构造 writeToDiskRunnable 的时候又会 mDiskWritesInFlight--,当为 1 的时候就说明前面的提交到内存的修改都已经提交的磁盘上了。那么来自 commit 的写磁盘任务就直接在当前线程即 UI 线程里执行了,如果前面还有写磁盘任务没完成,就和 apply 一样添加到 QueueWork 里,其实就是异步执行了。
所以对于 commit 操作来说,并不是绝对的就一定在 UI 线程执行,那这样有什么好处呢?
其实很好理解,如果先 apply 在紧接着 commit,那么如果不放在同一个线程中执行,就有可能导致 apply 的数据在 commit 之后被写入到磁盘中,磁盘中的数据是错误的,而且和内存中的数据不一致。
对于 apply 和 commit ,它是如何保证同步的呢?在这两个方法里都有 mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await(),它其实是一个 CountDownLatch。
关于它,我这里直接引用了网上的对它的介绍:
CountDownLatch 是一个同步工具类,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待,直到其他线程的操作执行完成后在执行。
OK,不要多说了。
关于添加和修改就完了,剩下就是取数据操作了:
SharedPreferencesImpl#getXxx :
@Override
@Nullable
public String getString(String key, @Nullable String defValue) {
synchronized (mLock) {
awaitLoadedLocked();
//直接从内存中取数据
String v = (String)mMap.get(key);
return v != null ? v : defValue;
}
}
总结:
- sSharedPrefsCache 是一个 ArrayMap<String,ArrayMap<File,SharedPreferencesImpl>>,它会保存加载到内存中的 SharedPreferences 对象,ContextImpl 类中并没有定义将 SharedPreferences 对象移除 sSharedPrefsCache 的方法,所以一旦加载到内存中,就会存在直至进程销毁。相对的,也就是说,SP 对象一旦加载到内存,后面任何时间使用,都是从内存中获取,不会再出现读取磁盘的情况
- SharedPreferences 和 Editor 都只是接口,真正的实现在 SharedPreferencesImpl 和 EditorImpl ,SharedPreferences 只能读数据,它是在内存中进行的,Editor 则负责存数据和修改数据,分为内存操作和磁盘操作
- 获取 SP 只能通过 ContextImpl#getSharedPerferences 来获取,它里面首先通过 mSharedPrefsPaths 根据传入的 name 拿到 File ,然后根据 File 从 ArrayMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> cache 里取出对应的 SharedPrederenceImpl 实例
- SharedPreferencesImpl 实例化的时候会启动子线程来读取磁盘文件,但是在此之前如果通过 SharedPreferencesImpl#getXxx 或者 SharedPreferences.Editor 会阻塞 UI 线程,因为在从 SP 文件中读取数据或者往 SP 文件中写入数据的时候必须等待 SP 文件加载完
- 在 EditorImpl 中 putXxx 的时候,是通过 HashMap 来存储数据,提交的时候分为 commit 和 apply,它们都会把修改先提交到内存中,然后在写入磁盘中。只不过 apply 是异步写磁盘,而 commit 可能是同步写磁盘也可能是异步写磁盘,在于前面是否还有写磁盘任务。对于 apply 和 commit 的同步,是通过 CountDownLatch 来实现的,它是一个同步工具类,它允许一个线程或多个线程一致等待,直到其他线程的操作执行完之后才执行
- SP 的读写操作是线程安全的,它对 mMap 的读写操作用的是同一把锁,考虑到 SP 对象的生命周期与进程一致,一旦加载到内存中就不会再去读取磁盘文件,所以只要保证内存中的状态是一致的,就可以保证读写的一致性
注意事项以及优化建议
- 强烈建议不要在 SP 里面存储特别大的 key/value ,有助于减少卡顿 / ANR
- 请不要高频的使用 apply,尽可能的批量提交;commit 直接在主线程操作,更要注意了
- 不要使用 MODE_MULTI_PROCESS
- 高频写操作的 key 与高频读操作的 key 可以适当的拆分文件,以减少同步锁竞争
- 不要连续多次 edit,每次 edit 就是打开一次文件,应该获取一次 edit,然后多次执行 putXxx,减少内存波动,所以在封装方法的时候要注意了
- apply 在 QueueWork 维护的单线程池调用,虽然是异步的但是可能会阻塞 Service.onStop 和 Activity.onPause 方法,可能会导致 ANR
ANR 容易发生的地方:
- sp.getXxx,首先会调用 awaitLoadedLocked 等待首次 sp 文件创建与读取操作完成
- sp.apply 虽然是异步的但是可能会在 Service Activity 等生命周期期间 mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await() 等待过久
- sp.commit 最终会调用 sp.writeToFile 方法,很耗时
- ContextImpl.getSharedPreferences,主线程直接调用的话,如果 sp 文件很大处理时间也就会变成
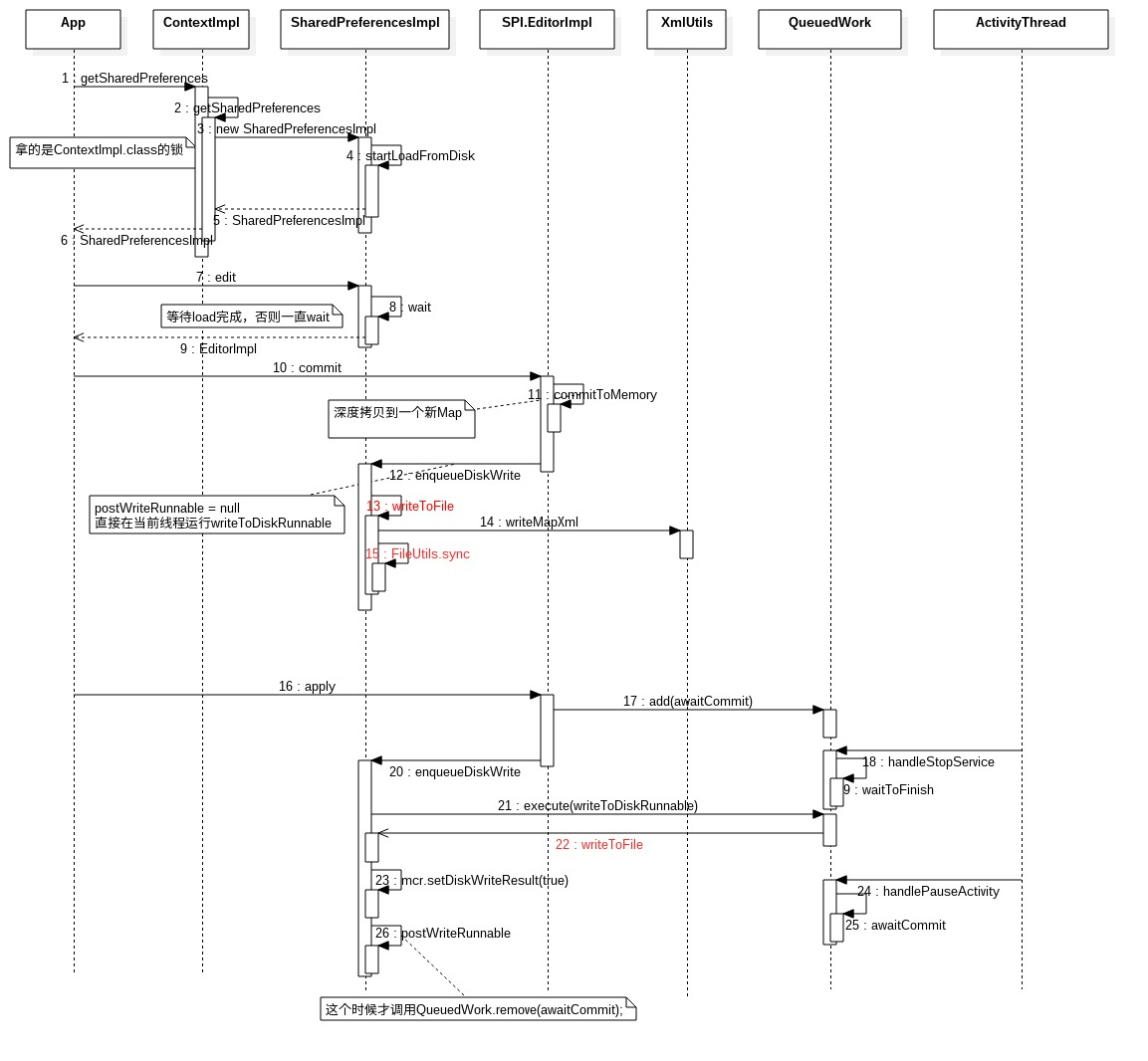
时序图
引自以下参考文章: